
HL Paper 1
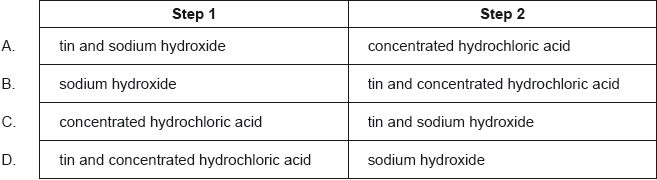
Which reagents are needed to convert nitrobenzene to phenylamine in 2 steps?
What is the number of optical isomers of isoleucine?
A. 0
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
Which statement is correct for a pair of enantiomers under the same conditions?
A. A racemic mixture of the enantiomers is optically active.
B. They have the same chemical properties in all their reactions.
C. They have the same melting and boiling points.
D. They rotate the plane of plane-polarized light by different angles.
Which molecule is chiral?
A. 2-chlorobutane
B. 2,2-dichloropentane
C. Propan-2-amine
D. 4-hydroxybutanoic acid
B. (CH3)3CCHO
C. (CH3)3COH
D. (CH3)3CCOC(CH3)3
Which two molecules are cis-trans isomers of each other?

A. X and Z
B. X and Y
C. W and Y
D. W and Z
Which halogenoalkane reacts the fastest with hydroxide ions in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
A. 1-chlorobutane
B. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
C. 1-iodobutane
D. 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
Which molecule exhibits optical isomerism?
A. 3-iodopentane
B. 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
C. 1,3-diiodopropane
D. 2-iodobutane
Propene is reacted first with hydrogen chloride to produce X which is then reacted with aqueous sodium hydroxide to give Y. Finally, Y is reacted with excess acidified potassium dichromate solution.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{HCL}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{NaOH(aq)}}}}{\text{Y}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}^ + }/{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{{\text{O}}_7}^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}}}}{\text{Z}}\]
What is the major product, Z?
A. CH3CH(OH)CH3
B. CH3COCH3
C. CH3CH2CHO
D. CH3(CH2)2COOH
Which molecule has a chiral centre?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH=CHCHO}}\)
B. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C=CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHOHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. (CH3)3CCHO
C. (CH3)3COH
D. (CH3)3COC(CH3)3
What is name of this compound applying IUPAC rules?
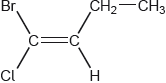
A. E 1-bromo-1-chlorobut-1-ene
B. Z 1-bromo-1-chlorobut-1-ene
C. E 1-bromo-1-chloro-2-ethylethene
D. Z 1-bromo-1-chloro-2-ethylethene
Which statements about substitution reactions are correct?
I. The reaction between sodium hydroxide and 1-chloropentane predominantly follows an \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\) mechanism.
II. The reaction between sodium hydroxide and 2-chloro-2-methylbutane predominantly follows an \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\) mechanism.
III. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with 1-chloropentane occurs at a slower rate than with 1-bromopentane.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which compound can exist as stereoisomers?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHO}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHOHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which isomers exist as non-superimposable mirror images?
A. cis-trans isomers
B. diastereomers
C. enantiomers
D. structural isomers
Which molecule exhibits optical isomerism?
A. 3-chloropentane
B. 2-chlorobutane
C. 1,3-dichloropropane
D. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
Which type(s) of stereoisomerism, if any, is/are present in the molecule CH2=CHCHBrCH3?
A. Optical only
B. Geometric only
C. Optical and geometric
D. Neither optical nor geometric
Which factors affect the rate of nucleophilic substitution in halogenoalkanes?
I. The nature of the attacking nucleophile
II. The identity of the halogen
III. The structure of the halogenoalkane
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What does a polarimeter measure?
A. Colour of reaction mixture
B. Polarity of a molecule
C. Configuration of a molecule as R or S
D. Rotation of plane-polarized light
Which reaction occurs via a free-radical mechanism?
A. \({{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_6} + {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2} \to {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{Br}} + {\text{HBr}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4} + {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2} \to {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_9}{\text{I}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_9}{\text{OH}} + {{\text{I}}^ - }\)
D. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_3})_3}{\text{CI}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{)}}_3}{\text{COH}} + {\text{HI}}\)
Halogenoalkanes can undergo \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\) and \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\) reactions with aqueous sodium hydroxide. Which halogenoalkane will react fastest with a \({\text{0.1 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) solution of aqueous sodium hydroxide?
A. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
B. 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
C. 1-chlorobutane
D. 1-iodobutane
What is the product of the reaction between pentan-2-one and sodium borohydride, NaBH4?
A. Pentan-1-ol
B. Pentan-2-ol
C. Pentanoic acid
D. Pentanal
Which compound could rotate the plane of polarization of polarized light?
A. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCl}}\)
What is the major organic product formed from the reaction of (CH\(_3\))\(_3\)CBr with a concentrated, ethanolic solution of KOH?
A. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COH}}\)
B. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CO}}\)
D. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHO}}\)
Which halogenoalkane reacts fastest with sodium hydroxide?
A. 1-iodobutane
B. 1-chlorobutane
C. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
D. 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
1-bromobutane, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}}\), can be converted to 1-aminopentane, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\), in a two-step process.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{Br}}\xrightarrow{I}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CN}}} \\ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow{{II}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}} \end{array}\]
What are the reagents I and II?
Which molecule contains a chiral carbon?
A. CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH3
B. CH3CH2CHBrCH3
C. CH2BrCH(CH3)CH2Br
D. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2Br
How many four-membered ring isomers are there of dichlorocyclobutane, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
What should be changed to alter the rate of nucleophilic substitution of tertiary halogenoalkanes?
A. The nucleophile
B. The concentration of the nucleophile
C. The concentration of the tertiary halogenoalkane
D. The size of the reaction flask
Which pair of isomers always shows optical activity?
A. Cis-trans
B. Enantiomers
C. Conformational
D. E/Z
Which compound is optically active?
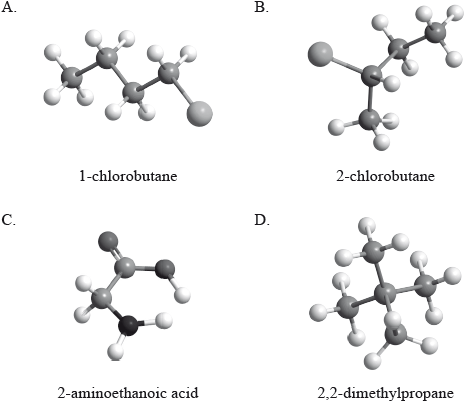
Which compound can exist as stereoisomers?
A. 1,2-dichloroethane
B. 1,1-dichloroethene
C. Butan-2-ol
D. Propan-2-ol
Which statement is correct about the enantiomers of a chiral compound?
A. Their physical properties are different.
B. All their chemical reactions are identical.
C. A racemic mixture will rotate the plane of polarized light.
D. They will rotate the plane of polarized light in opposite directions.
Which compound has a chiral carbon?
A. Propan-2-ol
B. 1-bromo-2-methylbutane
C. 3-bromopentane
D. Ethane-1,2-diol
What is the correct order for the increasing rate of hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes by dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCl}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CBr}}\)
B. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CBr}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
C. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCl}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CBr}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CBr}} < {{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCl}}\)
What is the name of the following compound applying IUPAC rules?
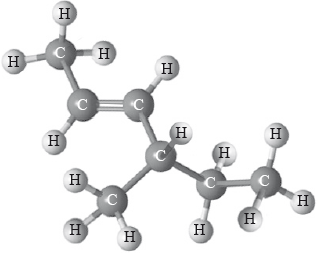
A. cis-4-methylhex-2-ene
B. cis-4-ethylpent-2-ene
C. trans-4-methylhex-2-ene
D. trans-4-ethylpent-2-ene
The hydrolysis of tertiary bromoalkanes with a warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution proceeds by a two-step \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}\) mechanism.
Step I: \({\text{R}} - {\text{Br}} \to {{\text{R}}^ + }{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}^ - }\)
Step II: \({{\text{R}}^ + } + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {\text{R}} - {\text{OH}}\)
Which description of this reaction is consistent with the above information?

What is the product of the reduction of 2-methylbutanal?
A. 2-methylbutan-1-ol
B. 2-methylbutan-2-ol
C. 3-methylbutan-2-one
D. 2-methylbutanoic acid
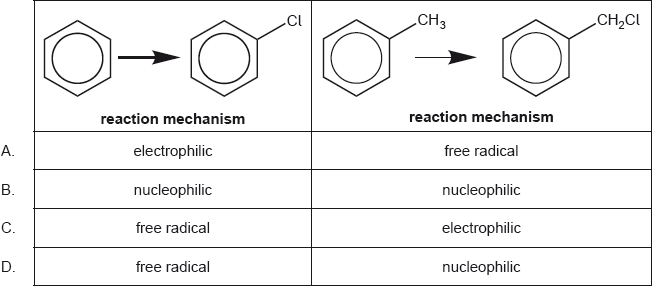
Which is the correct combination of substitution reaction mechanisms?
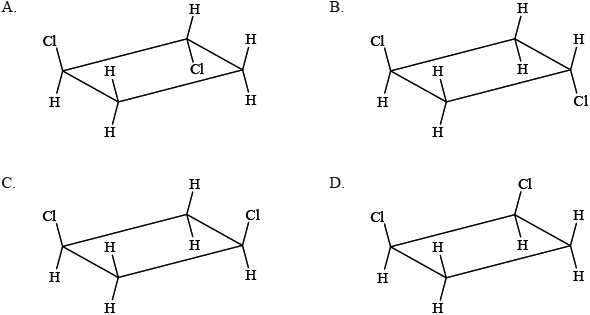
Which structure is a geometric isomer of cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane?
In which order should the reagents be used to convert benzene into phenylamine (aniline)?
Which statement about isomerism is correct?
A. But-1-ene and but-2-ene are geometrical isomers.
B. But-1-ene has two geometrical isomers.
C. Butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol are optical isomers.
D. Butan-2-ol has two optical isomers.
What effect of optical isomers on plane-polarized light can be measured using a polarimeter?
A. Reflection
B. Emission
C. Rotation
D. Absorption
Propanitrile can be prepared by reacting bromoethane with potassium cyanide. Which statement is not correct about the reaction between bromoethane and potassium cyanide?
A. The reaction is bi-molecular.
B. The reaction follows the \({{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}\) mechanism.
C. Homolytic fission occurs between the carbon-bromine bond in bromoethane.
D. The cyanide ion, \({\text{:C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }\), acts as a nucleophile.
Which statement is correct about the major reaction between 1-chloropropane, CH3CH2CH2Cl,
and dilute sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH (aq)?B. The hydroxide ion acts as a Brønsted–Lowry base.
C. The reaction has two distinct steps.
D. Water is a product.
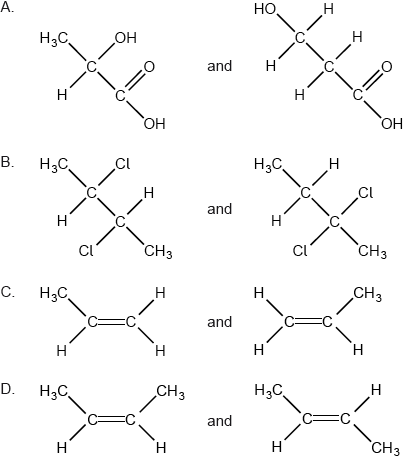
Which pair are geometric isomers?
Propene reacts separately with H2O/H+ and H2/Ni to give products X and Z respectively.
What are the major products of the reactions?
Which statement about stereoisomers is correct?
A. 1,2-dichloroethane has two geometrical isomers.
B. 1,2-dichloroethane has two optical isomers.
C. 1,2-dichloroethene has two geometrical isomers.
D. 1,2-dichloroethene has two optical isomers.
Which is correct for the conversion of propanal to propyl methanoate?